Socio-Environmental Innovation and Entrepreneurship Park
An architectural benchmark for energy efficiency and urban revitalization in Concón.
Place
Concón, Chile
Year
2017 - 2018

Objectives
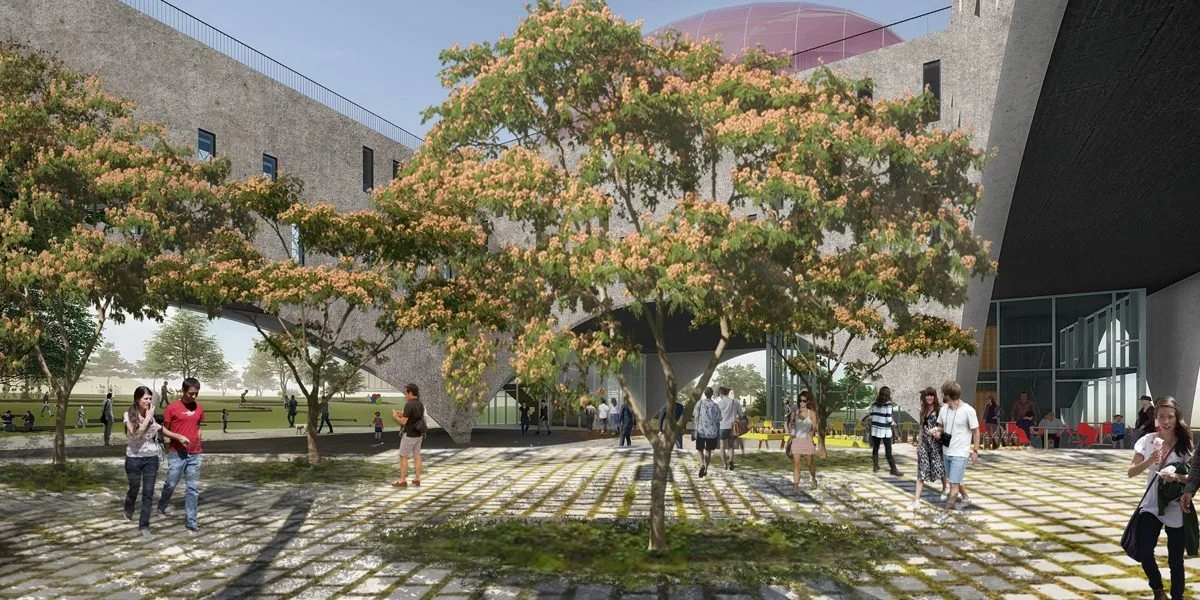
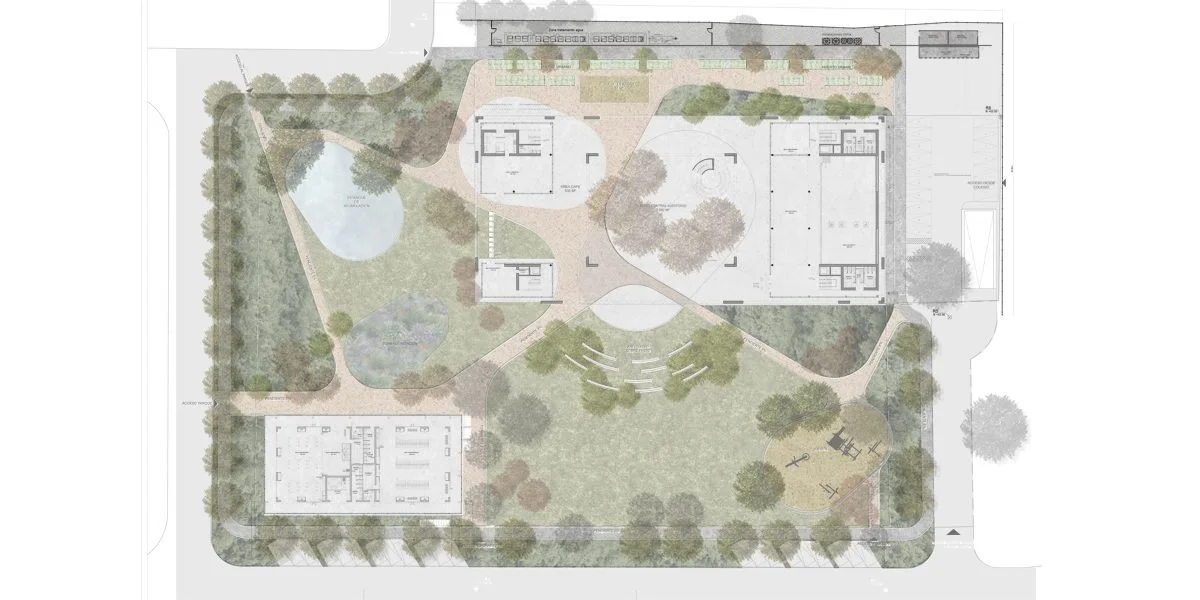
Transform a 14,000 m² disused site into a hub for innovation, entrepreneurship, and community gathering for the district of Concón.
Establish a world-class sustainability standard, creating a building capable of operating with minimal consumption of natural resources.
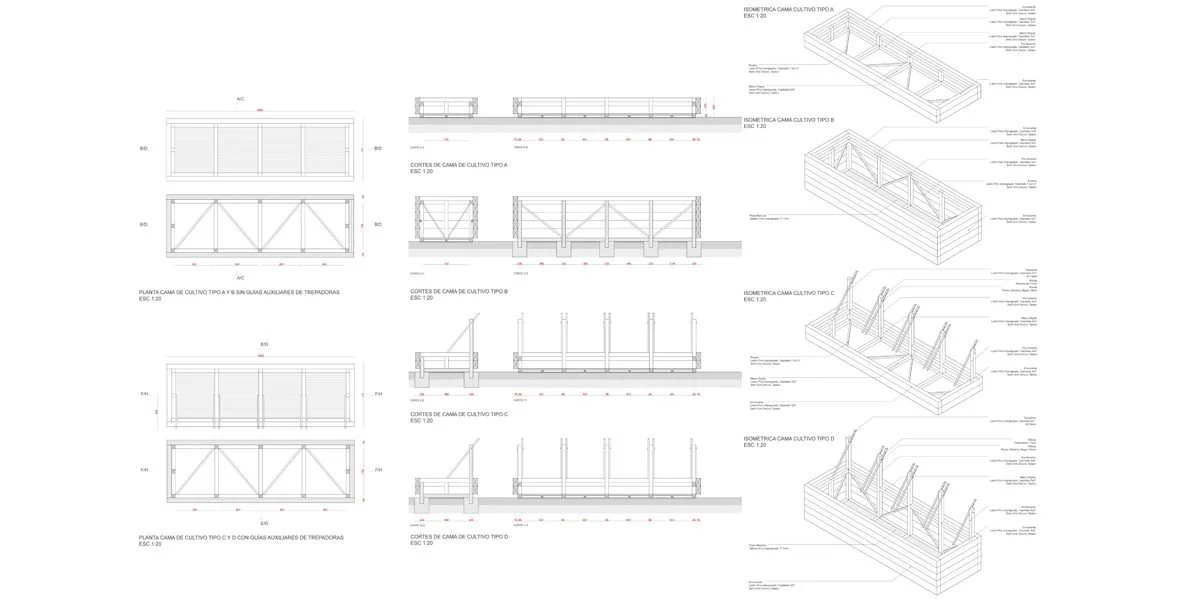
Integrate public space with urban farming, bringing nature and food sovereignty closer to residents through integrated greenhouses.
Demonstrate the viability of passive architecture, drastically reducing the carbon footprint in institutional construction.
Methodology
The park's design was based on bioclimatic architecture and circular economy strategies:
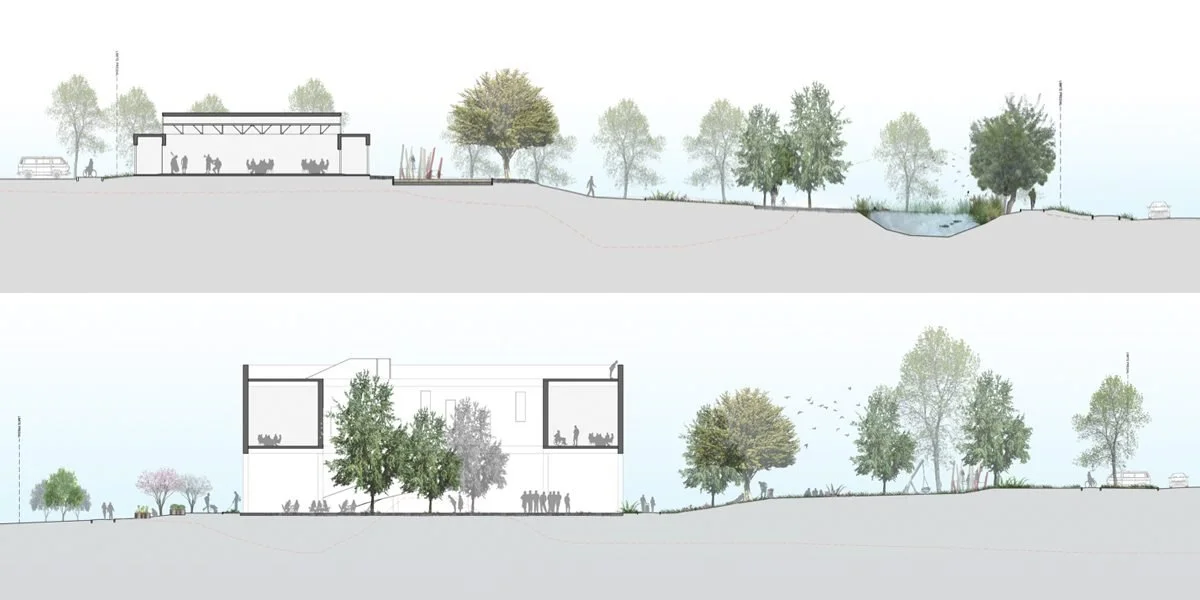
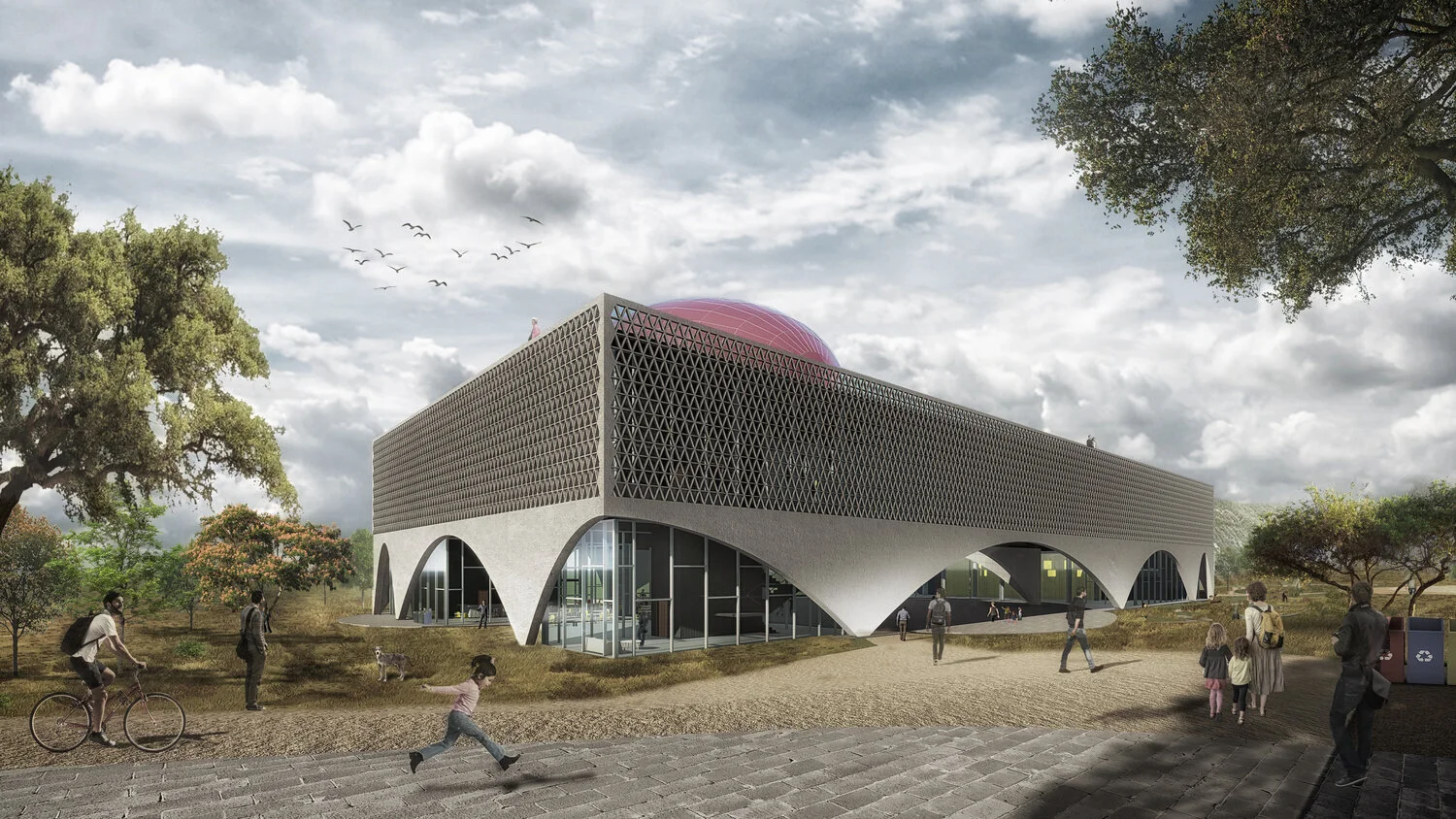
Thermal Facade Design: Implementation of a protective "skin" that filters solar radiation and promotes natural ventilation, eliminating reliance on mechanical climate control systems.
Closed Water Cycle: Integration of an on-site greywater treatment plant to guarantee the irrigation of the 14,000 m² park without using potable water.
Photovoltaic Energy Generation: Incorporation of a solar panel plant on the roof to cover a significant portion of the building’s electricity consumption.
Activation of Residual Land: Conversion of an abandoned site into cultural and environmental infrastructure linked to the Casa Abierta Cultural Center.
Cliente / Aliados
Location: Magallanes Avenue, Concón, Valparaíso Region.
Environment: Casa Abierta Cultural Center.
Design and Architecture: Ciudad Emergente.
Resultado e Impacto
Superior Energy Efficiency: 80% reduction in energy consumption compared to traditional standard buildings.
Critical Resource Savings:
Water: Annual savings of 10 million pesos in irrigation thanks to the on-site treatment plant.
Electricity: Reduction of over 3 million pesos per year in electricity costs through solar energy.
High-Impact Infrastructure: Creation of a massive public space for cultural events and outdoor activities in a previously underutilized area.
Urban Farming Greenhouse: Implementation of a pedagogical and productive space that allows for vegetable cultivation in the heart of the city.
Conclusiones
The Socio-Environmental Innovation and Entrepreneurship Park in Concón proves that cutting-edge architecture and ecological awareness can coexist in harmony. By prioritizing 80% energy savings and self-managed water systems, Ciudad Emergente proposes a development model where the building is not just a structure, but a living organism that contributes to community well-being and planetary balance. It is, ultimately, a benchmark for how cities can heal and renew their vacant lots through socio-environmental innovation.